preface
If you read each volume of the books that have been published so far, you can understand the fact that electromagnetic waves are a group of “electromagnetic elements” that are quantum beings, abandoning the conventional concept of electromagnetic waves.
Furthermore, as I emphasized in Volumes 3 and 8, I think you are convinced by the fact that even if the conductor is not directly connected to the power supply, an electric current will be generated if the “electromagnetic elements” comes into contact with the conductor.
It goes without saying that the same phenomenon occurs even in a direct current (or a square wave signal) in which the amount of the “electromagnetic elements” group does not change with time. This is also demonstrated in this book.
First, let’s talk about the antenna.
Considering the movement of the electromagnetic element group (mainly the magnetic field element in this case) on the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna, it can be seen that direct current (square wave signal) can also be transmitted and received.
I have always emphasized that the electromagnetic element is divided into a magnetic field element and electronic field element.
Next is the magnet. Considering this matter, it seems that the electromagnetic element is composed of a magnetic field element and a electronic field element rather than being divided into a magnetic field element and a electronic field.
Then, the theory of “solar cells” will be overturned.
A “solar cell” has an antenna and receives sunlight (so to speak, alternating current), which is its ultra-short wave alternating current.
As I wrote in Volume 6, if it is received as it is, it will become zero volt due to multiple reflection by the antenna or the resistor at the electric wire part from the antenna.
After receiving the electromagnetic element group with the antenna, for example, if only the positive current is taken out immediately, even if this positive current is reflected multiple times, it becomes a positive direct current and the solar cell can function.
Regarding magnetism, unlike the conventional theory, the current flowing through the coil flows symmetrically from the input end / output end to the coil, according to the theory of “Volume 4, New Capacitors and Coil”. Pushing forward with the fact, we can see that the electromagnetic element group is also functioning in the magnet. (Even after the current has been applied)
Afterword
Separating the “electromagnetic element” of the electromagnetic group into “magnetic field element” and “electronic field element”, and considering the movement of the “magnetic field element” on the antenna, I was able to construct a “new antenna theory“.
Although I have just started, I was able to construct a “new solar cell theory” by the same method for solar cells.
Furthermore, I was able to construct a “new magnet principle“.
When forming a magnet by passing a current through a general coil, the conventional theory was that the current flows unilaterally from the inlet to the outlet of the coil, but this is incorrect, and the coil inlet / outlet Positive / negative symmetric currents flow from both sides at the same time.
As a result, it will be as shown in the figure below.
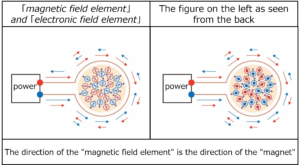
And finally, the positive / negative symmetric currents cancel each other out and the current becomes zero.
However, even if this current is interrupted, the “magnetic field elements” of these red and blue circles, in which “ferromagnets” are stored, still exert the “function of magnets“.
On the other hand, the “electronic field elements” exist in opposite directions (“red magnetic field element is inward” and “blue magnetic field element is outward”), and the total is zero volt, which is never detected by the external measurement system.
Therefore, the magnetic field from the magnet is an electromagnetic wave (a group of electromagnetic waves, a group of “magnetic fields”, and a group of “ electronic field element “). (The “electric field” is also generated from the “magnet”, but it is not observed.)
Regarding the fact that “magnetization exists even if the current is lost”, the fact that the “magnetic field” works without being affected by the outside should be considered as the same existence as gravity that works without being affected by the outside.
table of contents
Preface
Chapter 1 Electromagnetic waves are also generated from direct current
Introduction Misunderstandings about magnetic fields and electric fields
Section 1 Square wave signal is also a DC signal
Section 2 The principle of the antenna is the principle of power generation
Chapter 2 Consideration using a dipole antenna
Introduction Experimental antenna
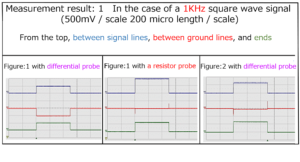
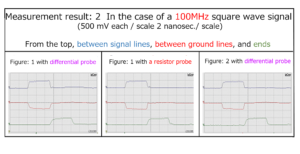
Section 1 Square wave signal transmission / reception experiment
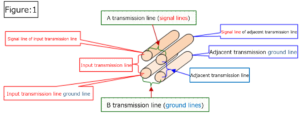
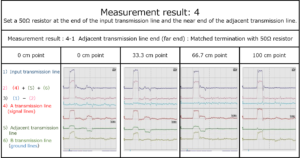
Section 2 Remeasure “Measurement results: 1-4” in the previous section
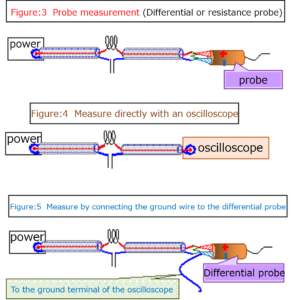
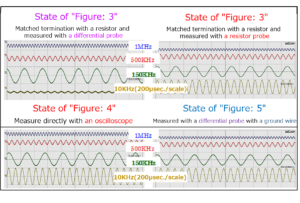
Section 3 Elimination of reflection phenomenon between antenna and coaxial cable for power supply / reception
Supplement: 1 In the case of continuous pulse
Supplement: 2 Matching resistance
Supplement: 3 Reception status when the resistance value of the insertion resistor (“Fig .: 1”) is changed.
Supplement: 4 When the coaxial cable on the receiving side is changed to a feeder line
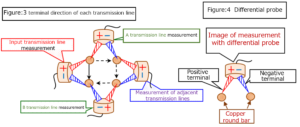
Section 4 Voltage status on the transmitting and receiving antennas
Supplement: One-terminal measurement of differential probe
Chapter 3 Reason why the length of the dipole antenna is 1/4 of the wavelength
From such a result, you can be convinced that the length of the dipole antenna is 1/4 of the wavelength.
(Even in the case of “Reception antenna length: 50 cm each”, the reception condition is slightly better.)
Chapter 4 Construction of a new theory regarding antennas
Section 1 In the case of transmitting antenna
Section 2 In the case of receiving antenna
Chapter 5 Difference between 010 wave and 0110 wave
Chapter 6 Exploration of New Solar Cell Theory
Supplement: Slowing up and down of AC and direct current
Section 1 The first step of the new solar cell theory
When there is only one receiving antenna and when there are two receiving antennas
Section 2 The second step of the empirical experiment of the new solar cell theory (Combining a diode with one antenna)
Chapter 7 New Magnet Principle
Introduction Doubts about how current flows through the coil of the conventional theory
Section 1 Inflow and outflow of current to the coil experiment in air)
Section 2 Examining the inside of the coil with an iron core coil instead of in the air
Section 3 Coil with more copper wire wound around the iron core
Section 4 Current and magnet flowing through the coil
Supplement: Magnetic field after turning off the power
Section 5 Hollow coil
Section 6 Conductor resistance
Item 1 The first cause of conductor resistance (reflection from diamagnetic material components in the conductor)
Item 2 The second cause of conductor resistance (depending on the ferromagnetic properties of the conductor)
Section 7 Electromagnetic field of iron core coil (while current is flowing)
Supplement: Electromagnetic field of aluminum coil (while current is flowing)
Chapter 8 Electromagnetic element is magnetic field element and electronic field element
Chapter 9 Group of electromagnetic element and current
Chapter 10 Residual “group of electromagnetic element” population on iron core
Chapter 11 Role of magnetic field and electric field
Chapter 12 Superconductivity
Supplement: what is disappointed
Main measuring instruments used, etc.
1 Pulse generator and function generator
2 Oscilloscope
3 SMA connector
4 Differential probe
5 EO (Electro-Optic-Sampling) probe
6 Coaxial cable
7 Parallel line: Red-black covered line
Afterword
| For more detailed information,
please contact: Soubunsha E-mail: info@soubunsha.com 窓文社(Soubunsha)Web site http://u33.sakura.ne.jp/soubunsyamakuji.htm 宇佐美保(Tamotsu Usami) Web site |


Recent Comments